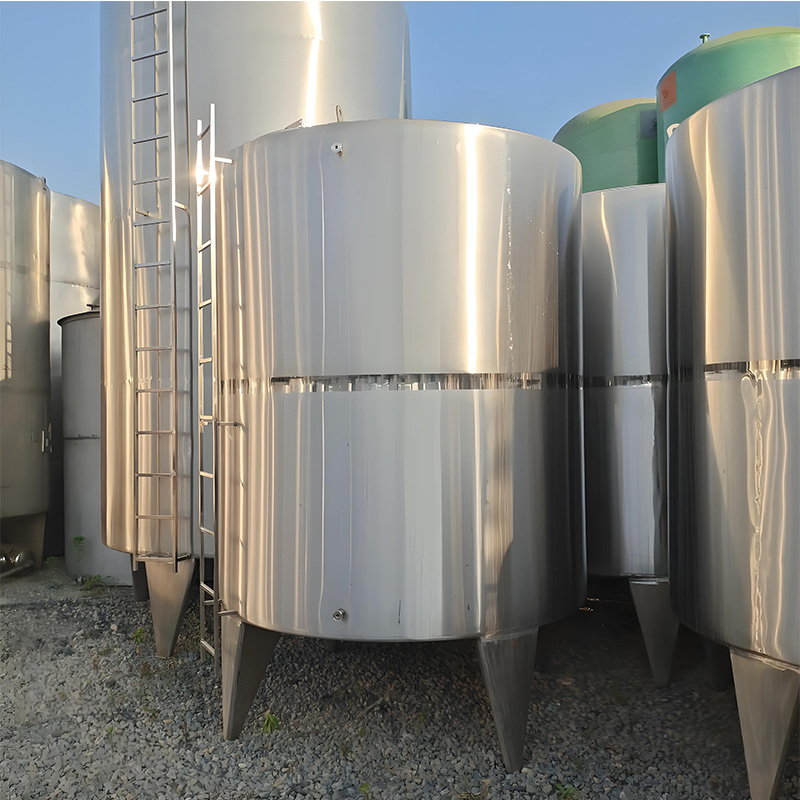
Stainless Steel Storage Tank: What Makes the Best Food-Grade Tank
2025/06/18
80 view
Food-Grade Stainless Steel Storage Tanks: 7 Critical Selection Factors
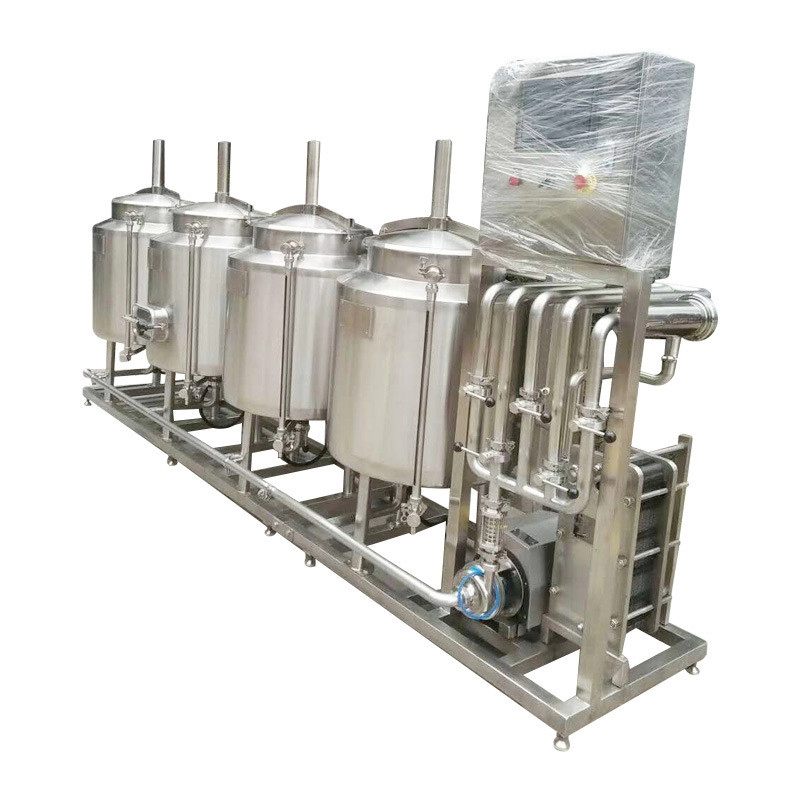
The 304 vs 316L Dilemma in Dairy Storage
During a 2025 brewery project, we discovered stainless steel storage tanks marked “304” actually contained only 17.5% chromium – below FDA requirements. Always demand:
- Mill test certificates with 18% Cr/8% Ni minimum
- 3.2B surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.8μm)
- Non-toxic elastomeric seals
Electropolishing: More Than Just Shiny Surfaces
FDA data shows electropolished tanks reduce bacterial adhesion by 63% compared to mechanically polished surfaces. Interestingly, 82% of food recalls involve poorly finished tanks. Our solution:
- Specify 15-25 μm removal during electropolishing
- Use passivation per ASTM A967
- Implement quarterly roughness verification
304 vs 316L Stainless Steel for Food Storage
| Property | 304 | 316L |
|---|---|---|
| Chloride Resistance | ≤50 ppm | ≤1000 ppm |
| Cost Premium | Baseline | +35-40% |
| Weld Corrosion Risk | High | Low |
⚠️ Critical Mistake Alert
Avoid threaded connections in food-grade stainless steel storage tanks – they trap particulates. Use orbital-welded joints instead.
5-Step Sanitation Protocol
- Pre-rinse at 60°C (140°F) for 10 mins
- Circulate 2% caustic solution at 70°C
- Acid rinse (pH 2.5-3.0) for descaling
- Final rinse with <0.5 ppm chlorine water
- Steam sterilize at 121°C for 20 mins
Food Safety Compliance Checklist
- □ NSF/ANSI 51 certification
- □ Full radius corners (no sharp angles)
- □ Drain slope ≥2°
- □ CIP system validation records
FAQs: Food-Grade Tank Selection
Q: How often should I replace tank liners?
A: Replace FDA-approved liners every 3-7 years based on abrasion checks.
Q: Can I store acidic foods like tomatoes?
A: Yes, but only in 316L tanks with pH monitoring and annual passivation.