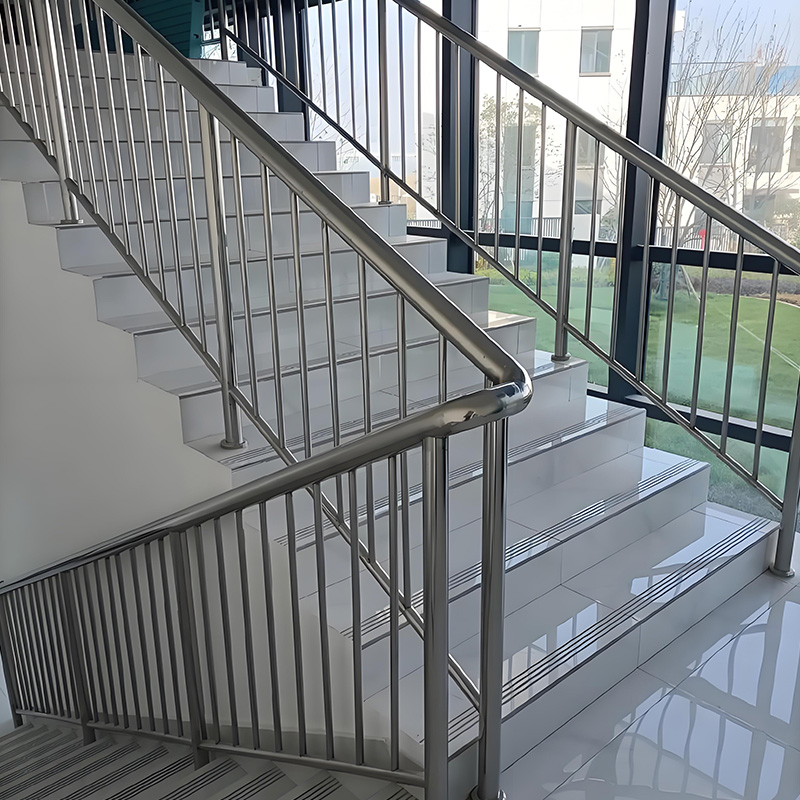
Stainless Steel Handrail Stairs: 4 Must-Know Installation Secrets
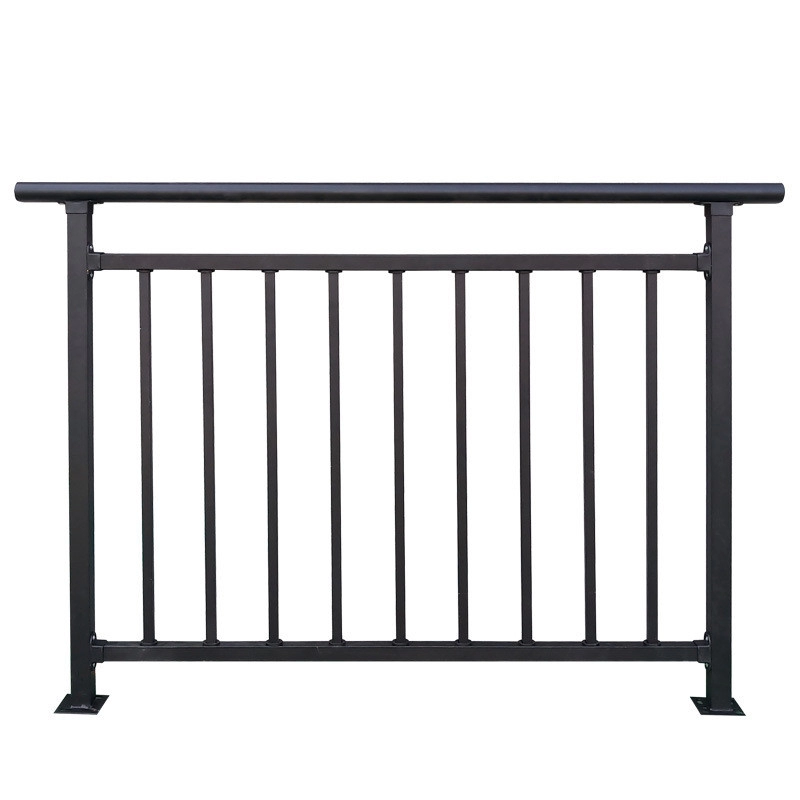

Installing stainless steel handrail stairs combines safety compliance with modern design—but one wrong step can compromise both. As demand for corrosion-resistant, low-maintenance solutions grows, professionals are discovering critical installation insights that make or break projects. Let’s uncover the proven techniques that separate flawless installations from costly mistakes.
The Science Behind Your Stainless Steel Handrail
Not all stainless is created equal. Grade 304 remains popular for indoor stairs due to its cost-effectiveness and decent corrosion resistance. But for coastal areas or de-icing salt exposure, Grade 316’s molybdenum content (2-3%) provides superior protection against chlorides. This matters because we’ve seen 304 failures in pool areas within 18 months where 316 lasted 10+ years.
Interestingly, surface finishes impact longevity too. While mirror polish looks stunning initially, brushed (Scotch-Brite) finishes better conceal scratches and fingerprint smudges in high-traffic areas. For external stairs, consider passivation treatments—a chemical process that enhances the natural protective oxide layer, reducing rust risk by over 60% according to industrial studies.
Our team encountered a baffling corrosion case in 2025: a newly installed luxury hotel’s stainless steel handrail stairs showed rust-like stains. Forensic analysis revealed carbon steel contamination from tools during fabrication—proof that dedicated stainless tools (wire brushes, grinding discs) are non-negotiable.
| Property | 304 Stainless | 316 Stainless |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good for most indoor environments | Excellent (resists chlorides/salts) |
| Key Alloy | 18% chromium, 8% nickel | 16% chromium, 10% nickel, 2-3% molybdenum |
| Cost Difference | Standard pricing | ~20-30% higher than 304 |
| Best Applications | Indoor stairs, low-humidity areas | Coastal regions, poolside, de-icing salt zones |
Safety Codes You Can’t Afford to Ignore
Compliance isn’t just paperwork—it prevents falls and liabilities. International building codes (IBC) and GB 4053.3-2009 mandate specific dimensions for stainless steel stair railings:
- Height: Minimum 900mm for platforms under 2m; 1050mm for 2-20m heights; 1200mm for over 20m elevations.
- Load Capacity: Top rails must withstand 890N concentrated or 700N/m distributed loads without failing.
- Gap Control: Openings between rails ≤500mm to prevent child entrapment.
Surprisingly, handrail diameter affects grip safety. Research with 51 female users showed optimal diameters between 30-50mm (1.75″-2″), with 32mm (≈1.25″) ranking highest for comfort and control. Non-circular profiles must have rounded edges (≥3mm radius) to avoid cutting into hands.
Warning: Never sacrifice safety for aesthetics! A client ignored kickplate requirements on glass-infilled stairs, resulting in a $12K OSHA fine when tools fell through gaps onto workers below. Always install ≥100mm high kickplates in commercial settings.
Step-by-Step Installation Mastery
Rushing installation causes wobbles and failures. Follow this professional sequence:
Pre-Installation Planning
Verify structural mounting points using blueprints. For concrete stairs, scan for rebar conflicts using a rebar detector. Pro tip: Order 10% extra stainless fasteners—mixing carbon steel bolts invites galvanic corrosion.
Mounting Post Installation
Anchor posts using through-bolt or back-panel methods. On finished surfaces, use diamond-core drills with water cooling to prevent tile/marble cracks. Posts spacing ≤1,000mm centers is critical for load distribution.
Rail Assembly Techniques
For curved sections, heat-bend rails using specialized blankets (15-20 mins at 300°F). Cold bending causes work hardening and micro-cracks. Use laser levels to align top rails—human eyesight error averages 3mm per meter.
Finishing and Inspection
Weld polishing should progress through 3 grit stages (80→220→400). Passivate all welds with nitric acid gel to restore corrosion resistance. Finally, conduct a “shake test”—any visible movement means reinforcement is needed.
Design Innovations and Problem Solvers
Modern stainless steel handrail stairs blend materials brilliantly. Hybrid designs with integrated wood caps (oak/walnut) add warmth while maintaining structural strength. For frameless glass systems, U-channel bases secured with structural silicone provide invisible support.
Counterintuitively, small details make big impacts. Self-leveling adjustable collars compensate for uneven floors up to 3.5mm—saving hours of shimming. Magnetic levitation systems like Ironlev® enable zero-friction sliding doors in integrated railing systems, perfect for accessible entries.
When noise is a concern (e.g., museums), isolate metal contacts using nylon sleeves or rubber grommets. One hospital project cut stair vibration noise by 70% using this approach.
Stainless Steel Handrail Stairs: Installation Checklist
✅ Verify material certificates match project specs (304 vs 316)
✅ Confirm post spacing ≤1,000mm per safety codes
✅ Use dedicated stainless tools to prevent contamination
✅ Passivate all welds and mechanical cuts
✅ Test load capacity with simulated 890N force
✅ Install kickplates where tools/objects may fall
✅ Apply protective film until project handover
FAQs: Stainless Steel Stair Handrails
Do stainless steel handrails rust?
Properly maintained 304/316 resists rust, but contamination, chlorine exposure, or lack of passivation can cause staining. Annual cleaning with oxalic acid solutions removes surface oxides.
Can I install stainless railings on existing stairs?
Yes! Retrofit kits use bolt-on base plates that avoid destructive concrete coring. Ensure your structure can handle lateral loads—consult an engineer if unsure.
Are glass panels compatible with stainless handrails?
Absolutely. Use 12mm+ tempered glass with silicone or stainless U-channels for clamping. Avoid metal-to-glass hard contact with nylon spacers.
Final Thoughts
Mastering stainless steel handrail stairs requires equal parts materials science, code knowledge, and precision craftsmanship. By selecting the right alloy, respecting load dynamics, and executing meticulous installations, you create timeless structures that protect users for decades. After all, the best handrail is one you never notice—it simply feels secure, looks elegant, and withstands the test of time.