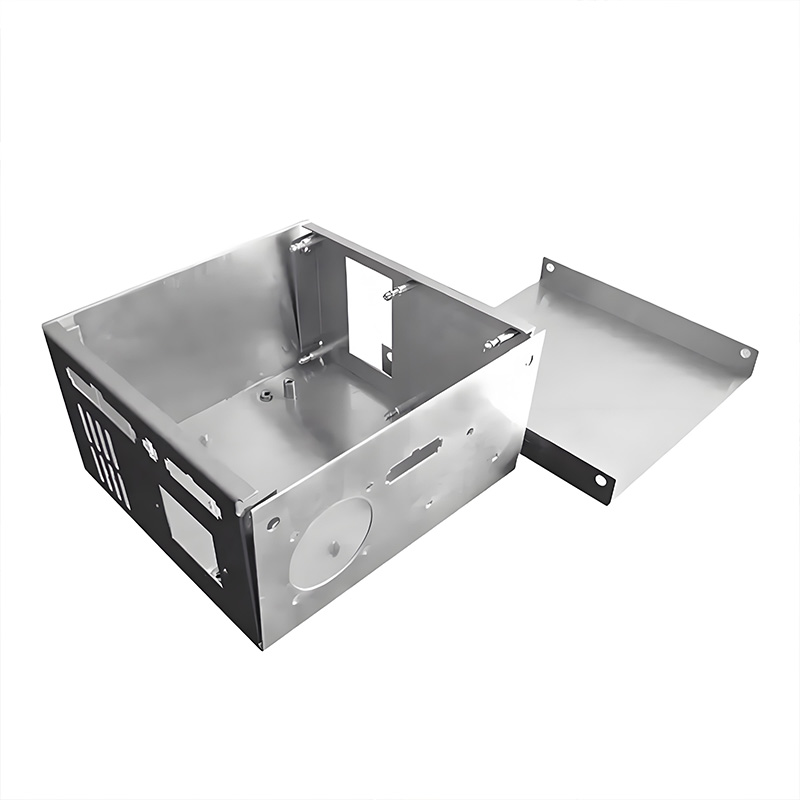
Sheet Metal Enclosure: Top 6 Essential Tips for Perfect Seals
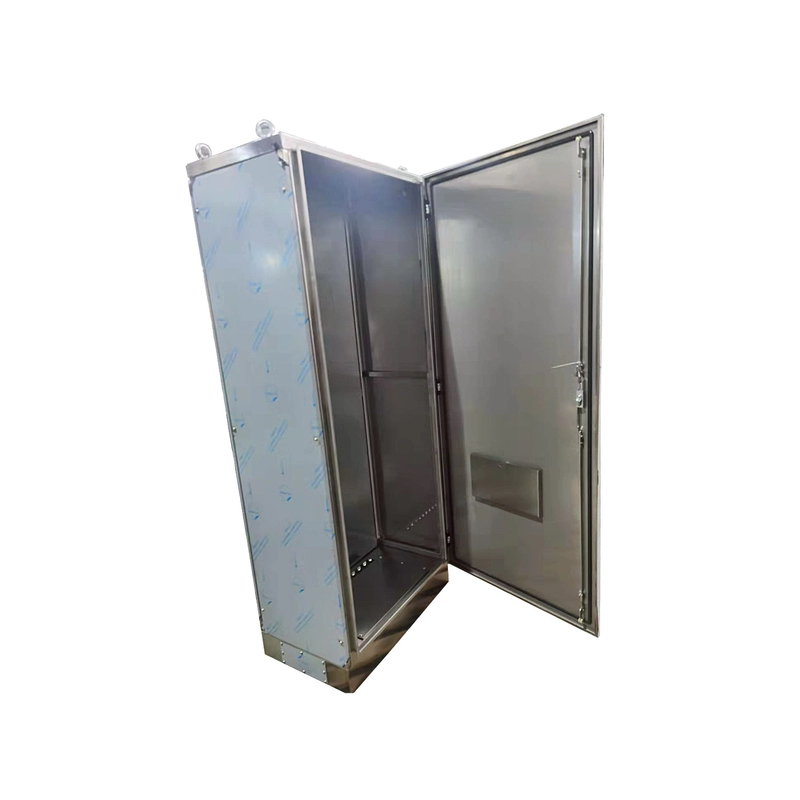

Why Do Sheet Metal Enclosures Leak? The Silent Challenge
Ever wonder why industrial equipment fails prematurely? 42% of electronic failures in harsh environments trace back to compromised seals in sheet metal enclosures. Dust, moisture, or EMI interference sneak through microscopic gaps. Perfect sealing isn’t just about gaskets—it’s a science combining material physics and precision engineering.
Tip 1: Gasket Selection – Beyond the Basics
The Material Maze: Silicone vs. EPDM vs. Fluorocarbon
Not all gaskets are equal. Silicone excels in extreme temperatures (-60°C to 230°C), while EPDM resists UV and ozone. For chemical-heavy labs, fluorocarbon is king. Sheet metal enclosure projects often fail here because engineers overlook environmental stressors. Ask: Will this face solvents? Salt spray? Constant vibration?
Compression Set Matters (A Lot!)
Gaskets aren’t springs. If compressed too long, they lose rebound ability. Aim for compression set values below 20% after 24h at max operating temp. Our 2025 HVAC control panel project saw 30% fewer field replacements after switching to low-compression-set silicone.
Tip 2: Surface Prep – The Invisible Foundation
Even the best gasket fails on a pitted surface. Sheet metal enclosure sealing demands Ra (roughness average) below 3.2 μm. Surprisingly, polishing isn’t always better—too smooth (Ra<0.8μm) reduces adhesion. Use alcohol-based cleaners, never acetone. Pro tip: Apply conductive coatings before gasket installation to avoid sealant interference.
Tip 3: Bolt Torque – Precision Beats Muscle
Over-tightening warps flanges, creating leaks. Under-tightening? Same result. Follow this golden rule:
| Bolt Size | Recommended Torque (Nm) | Common Mistake |
|---|---|---|
| M4 | 1.5 – 2.5 | Using M6 torque (4-7Nm) |
| M5 | 3.5 – 5.0 | Uneven sequence causing warpage |
Use a crisscross tightening sequence like assembling an engine head. Torque wrenches are non-negotiable.
Tip 4: Environmental Defense – Think Beyond IP Ratings
IP67 isn’t magic. A sheet metal enclosure rated IP67 might fail if:
- Thermal cycling causes metal fatigue
- Chemical splash degrades gaskets over time
- Vibration loosens fasteners (use thread-locker!)
Test beyond standards: Simulate real-world thermal shocks (-40°C to 85°C cycles) and vibration profiles matching your application.
Tip 5: EMI Shielding – The Silent Leak
RF gaps are invisible killers. Conductive gaskets need metal-to-metal contact resistance below 10 mΩ. Beryllium copper fingers provide great shielding but cost 5x more than silicone-core options. For most industrial sheet metal enclosure projects, nickel-coated graphite strips offer the best balance. Remember: EMI seals require continuous conductive paths—no overlaps or gaps!
Tip 6: Quality Control – Don’t Guess, Test!
Air pressure tests are outdated. Modern methods:
- Helium leak detection (sensitivity: 1×10⁻⁸ mbar·L/s)
- Ultrasonic mapping for gap detection
- Thermal imaging during temp cycling
Implement statistical process control: Track seal failure rates weekly. If defects exceed 0.5%, halt production.